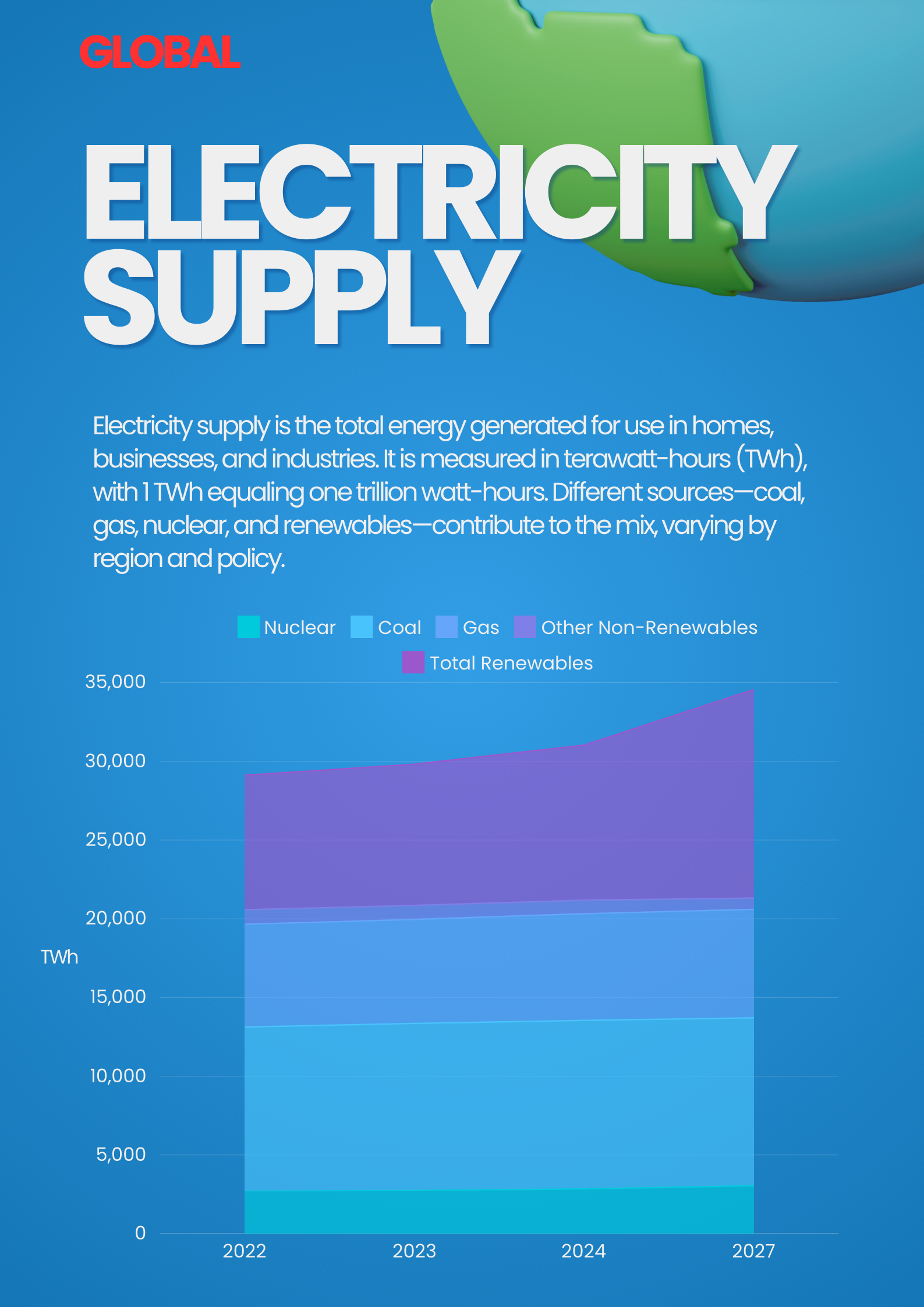
Global Electricity Supply (2022-2027)
Trends (2022-2024):
Coal remains the dominant source of electricity globally, increasing from 10,437 TWh in 2022 to 10,704 TWh in 2024, though growth is slowing.
Renewables show strong expansion, rising from 8,543 TWh in 2022 to 9,848 TWh in 2024, highlighting the rapid adoption of clean energy.
Nuclear energy sees steady growth from 2,686 TWh in 2022 to 2,840 TWh in 2024, reflecting investment in new reactors and higher utilization rates.
Gas increases moderately from 6,525 TWh in 2022 to 6,777 TWh in 2024, suggesting its continued role in balancing power supply.
Other non-renewables are in decline, falling from 927 TWh in 2022 to 860 TWh in 2024, as the shift away from inefficient fossil fuels continues.
Future Projections (2025-2027):
Renewables are expected to see the most significant growth, reaching 13,250 TWh by 2027, further increasing their global share.
Nuclear continues its upward trend, reaching 3,036 TWh by 2027, as nations expand low-carbon baseload capacity.
Coal generation is projected to remain relatively stable, slightly decreasing to 10,674 TWh by 2027 due to policy and economic shifts.
Gas continues modest growth, reaching 6,889 TWh by 2027, maintaining its role as a transitional fuel.
Other non-renewables decline further to 717 TWh by 2027, reinforcing the shift toward cleaner alternatives.
Electricity Supply and TWh
Electricity supply is the total energy generated for use in homes, businesses, and industries. It is measured in terawatt-hours (TWh), with 1 TWh equaling one trillion watt-hours. Different sources—coal, gas, nuclear, and renewables—contribute to the mix, varying by region and policy.
Click image for full view in new tab
Data from IEA - Electricity 2025